- Harley St, Port Harcourt, 500101, Rivers
- +234 0815 149 1555
- info@rsuth.ng

INSTITUTE OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
THE MPOX SCREENING APP
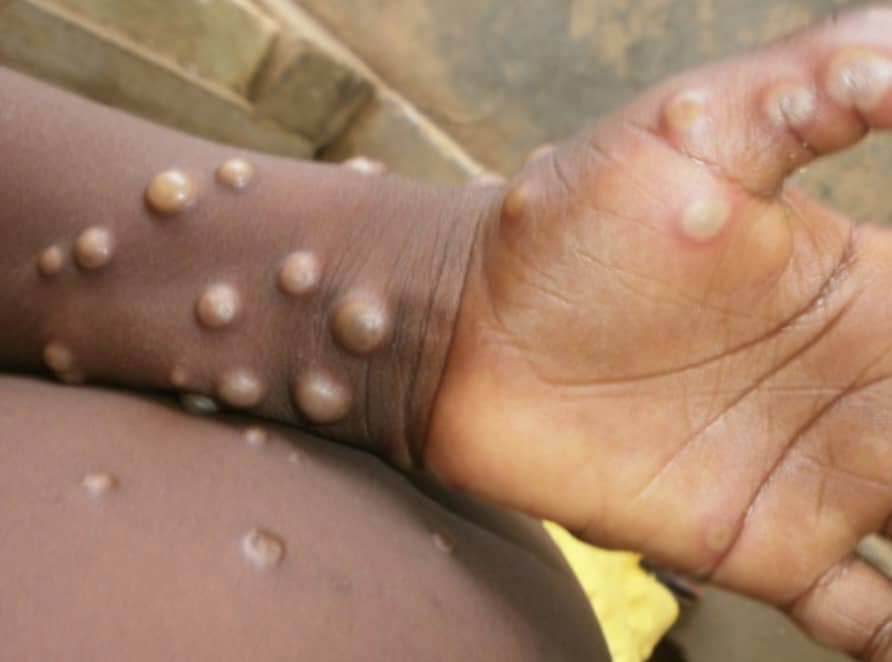
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a zoonotic viral disease caused by the Mpox virus (MPXV), an Orthopoxvirus related to smallpox. It is endemic in parts of Central and West Africa, including Nigeria, where it poses a significant public health challenge. The disease is characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, and a distinctive vesiculopustular rash. Transmission occurs through direct contact with infected animals, human-to-human spread via respiratory droplets, and contact with contaminated materials. Ecological factors tsustain viral reservoirs among rodents and other animals.
Nigeria experienced a major Mpox outbreak in 2017 after nearly 40 years without reported cases. Since then, sporadic outbreaks have continued to occur, with cases recorded in multiple states including Rivers State. , Nigeria (and Rivers State) remains one of the countries (and State respectively) with the highest Mpox burden in Africa, with cases affecting diverse population groups. Mpox has been declared a disease of public health importance by the World Health Organisation due to the potential for pandemic spread, significant risk of morbidity, and socioeconomic impact. The disease places a heavy strain on the healthcare surveillance system, and social system in the society. It also has implications for global health security, as evidenced by its unlimited spread.
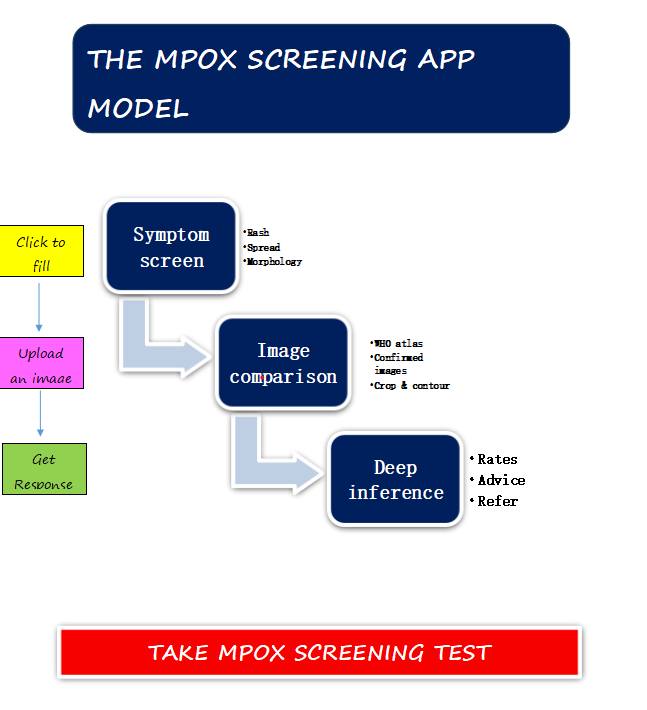
Early this year a team of the IIDRD conceived the idea of a surveillance tool for MPOX screening as a simple screening tool leveraging on the remarkable internet penetration and rich access to smartphones in the region. The major aims were to create awareness around MPOX, improve health-seeking behaviour and get individuals to take some responsibility for their health. The app, still in its web form is a screening and not a diagnostic tool. Diagnosis of Mpox is by PCR analysis. Yet it offers a humungous opportunity for case finding, and reduction of missed opportunities which are key factors in disease control intervention. The app holds great promise as a result of its robust design, being a learning app improved by feedback and requires no special expertise for operation

Core Model
The app uses deep learning techniques to classify images into risk categories, assisting healthcare professionals in decision-making designed to give traction without overloading the regional surveillance team having a high validity and reliability from recent testing. The model is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) trained to classify skin lesion images as High-Risk Mpox, Low-Risk Mpox, or Non-Mpox. It is based on EfficientNet due to its high accuracy and computational efficiency.
- Preprocessing Pipeline
- Image Resizing: Standardized to 224×224 pixels.
- Normalization: Pixel values scaled between 0 and 1.
- Data Augmentation: Rotation, flipping, contrast enhancement to improve robustness.
- Training Data
- Sources: Medical datasets with annotated images of Mpox, other skin conditions, and normal skin.
- Dataset Split:
- 80% Training
- 10% Validation
- 10% Testing
- Augmentation Techniques:
- Random Rotation ±30°
- Brightness/Contrast Adjustments
- Gaussian Noise Injection
- Model Training
3.1 Loss Function & Optimizer
- Loss Function: Categorical Cross-Entropy
- Optimizer: Adam with learning rate 0001
- Batch Size: 32
- Epochs: 50
3.2 Performance Metrics
- Model Inference
4.1 Input & Output
- Input: Single image (JPEG, PNG, or BMP)
- Output: Risk classification with confidence score
Example Output:
{“classification”: “High-Risk Mpox”, “confidence”: 0.87}
- Deployment
5.1 Stack
- Framework: TensorFlow/Keras
- Backend: FastAPI (Python)
- Frontend: React.js
- Database: PostgreSQL (stores metadata)
- Hosting: Dockerized container on AWS/GCP
5.2 Model Serving
- Deployed using TensorFlow Serving
- API containerized using Docker
- Load balanced with NGINX
- Security & Compliance
- Data Encryption: AES-256 for stored images, TLS for transmission.
- Access Control: Role-based authentication.
- Compliance: NDPR-compliant data handling.
- Future Improvements
- Expand dataset to improve generalization.
- Implement active learning for continuous model improvement.
- Optimize for mobile deploymentto assist field workers.
Conclusion
This AI-powered image classification model provides an early risk assessment for Mpox. It enhances clinical decision-making but it is by no means a replacement for professional surveillance or diagnosis. Future improvements will focus on dataset expansion, real-time mobile inference, and integration with hospital management systems.
Developers
- Golden Owhonda – Associate Professor of Public Medicine, Rivers State University (Director, IIDRD)
- Japhet Rusell – Dataxisng Nig Ltd
-
Find a clinic near you
-
Call for an appointment!
-
Feel free to message us!
About Us
Rivers State University Teaching Hospital formally Braithwaite Memorial Specialist Hospital (BMSH) is a government owned hospital, was named after Eldred Curwen Braithwaite, a British doctor and a pioneer of surgery.
- Rivers State University Teaching Hospital.
Additional Links
- Extention of RSUTH internship application deadline to 17th April, 2025 April 3, 2025
- A 3-Day Craniofacial Surgery Workshop April 3, 2025
- Congratulations to Dr. Linda Ireogbu-Emeruem (HOD Surgery RSUTH) March 20, 2025
- Celebrating H.O.D of the Month of January 2025 March 14, 2025
- World Dietitians Day 2025 March 13, 2025
